Conservation and ecological landscape of Gandhisagar Lake, Warora



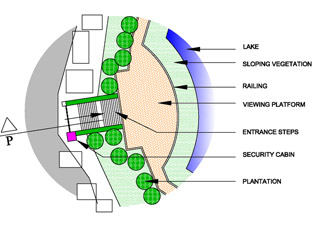
The design proposal addresses three key areas of concern, which are Ecological, Social and Economic. The proposal includes various methods to augment the water quality and quantity of the lake. Ecological restoration, prevention measures for soil erosion, soil conservation, beautification of lake and the Lake front and development of the existing infrastructure, to enhance public awareness, nature interpretation centre, monitoring programs etc. are the key features. The main objective is to conserve and maximize the resource for the city of Warora not only as a precious water resource but also as the socio cultural hub for the city.
Warora, Chandrapur District, Maharashtra
Commissioned by – Warora Muncipal Council
Gandhisagar Lake lies in the midst of Warora town, within Chandrapur district. This district is famous for its temples and forts and also due to its closeness to wildlife parks, mainly the Tadoba Tiger Reserve. Anandvan ashram, a community rehabilitation centre for leprosy patients founded by Baba Amte, is only 2 kms away from the lake.
Gandhisagar Lake was a perennial water body, of which today the size has reduced to one third of its original area, neither has it remained perennial. It is currently being heavily encroached upon by not only informal development but also legal authorized buildings, which today sit into the lake area; as is seen in the satellite image. Sewage water and defecation are the major sources of pollution, which has triggered hyacinth growth in the lake. Also siltation has resulted in reducing the water retention capacity of the lake. This has affected fishing and agricultural activities in and around the lake. Shingada crop is cultivated within the lake.
The Gandhisagar lake is sensitive to the effects of a broad range of environmental pollutants from adjoining forest land and urban runoff, industrial and municipal facilities, spills, and hazardous waste sites. The large surface area of the lake also makes it vulnerable to direct atmospheric pollutants like wet deposition and dry deposition on the lake surface or within the extensive land drainage system.
Gandhisagar Lake is rich in its ecological aspect as well as biodiversity due to fishing and shingada farming within the lake and also the presence of indigenous and native species of vegetation. Many kind of migratory and resident migratory birds are seen in the lake area.